SEO (Search Engine Optimization): An Ever-Changing Strategy


Much has changed over the years in how search engines like Google, Yahoo, Bing, and Baidu crawl, index, and rank webpages in their search engine results. Maximizing your company’s exposure in search engines is critical to achieving your business revenue goals.
Consider this:
- 90% of searchers have not made their mind up about a brand before starting their search. (Status Labs, 2018)
- 97% of people learn more about a local company online than anywhere else. (Source: SEO Tribunal)
- 70% - 80% of search engine users are only focusing on the organic results (MarTech, 2018)
- The first page of search engine results accounts for 71.33% of organic clicks (Smart Insights, 2020)
Bottom Line: The majority of your potential buyers who do not know you may not learn about your products and services unless you show up on page 1 in Google’s organic search results.
The Fundamentals of SEO
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) relates to the organic search listings that show up on a Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
There are different types of SERPs, which we will cover in more detail later in this article.
What’s the Difference between Organic Search and Paid Search?
Paid search ads are a form of advertisement on search engines based primarily on the keywords or phrases chosen for your ads, along with your ad budget and ad performance.
One of the key differences in paid search ads is that results (clicks on ads to your website or landing page) can be achieved much quicker than trying to get new pages ranked high in organic search results. Your ads will normally show up very shortly after you activate the ads.
Also, in paid search ads, you are typically charged on a per-click basis, thus the phrase Pay-Per-Click (PPC).
SEO efforts can take weeks, months, and even years, depending upon your success and performance on the fundamentals that we will cover in this article. That’s the bad news about SEO.
But the good news is that once your webpage is listed high in the organic listings through your SEO efforts, you do not have to pay each time someone clicks on your listing. Hundreds and even thousands of visitors can come to your website through your organic listings without you having to spend money each time someone clicks on your listing.
So how do you know which listings are considered organic and which are considered paid advertisements?
Here is a search engine results page that shows you the SEO (organic) listings and the paid ad listings (PPC) on a SERP. Search engines will normally show the paid ads above the organic ads. They will also sometimes show additional paid ads at the bottom of the page after the organic listings.
Each paid advertisement will be identified with the word Ad in bold to the left of the ad.
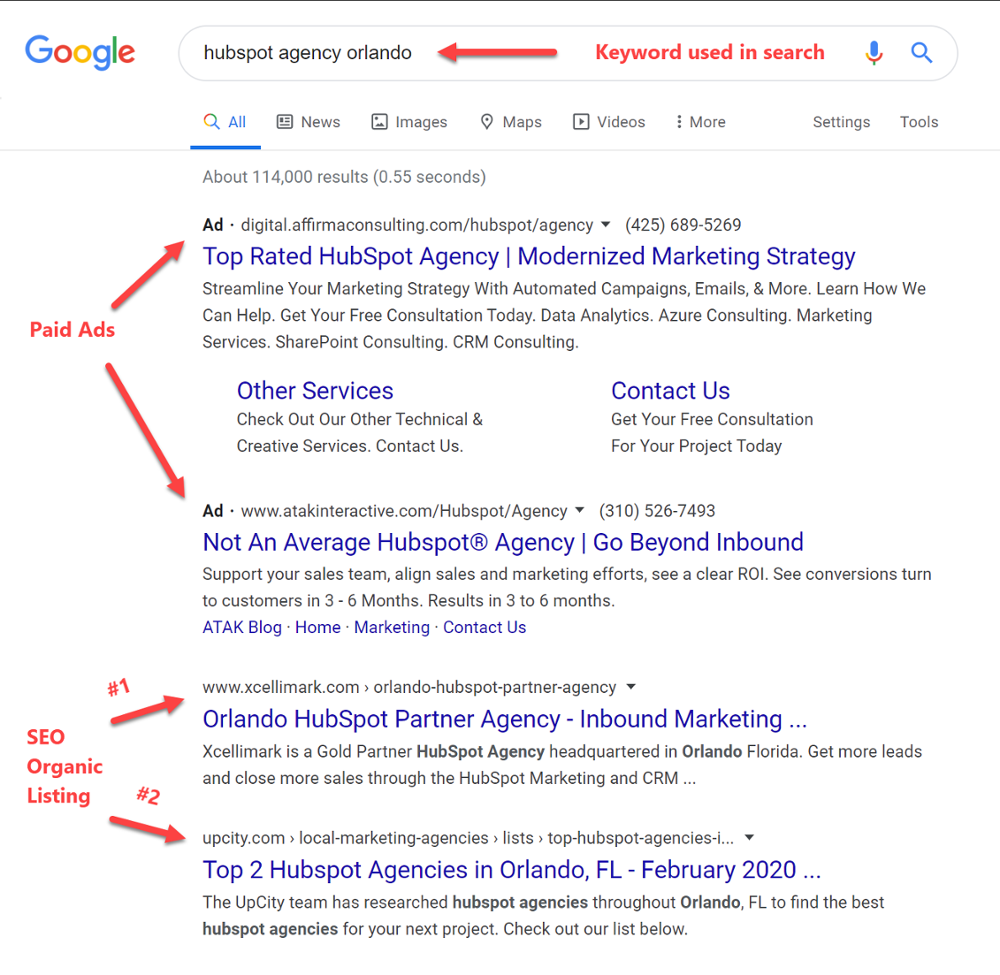
While search engine results can be achieved quicker through PPC, organic search results from SEO can achieve a higher ROI over the months and years.
Roughly 70% - 80% of searchers click on the organic listings versus 20% - 30% of searchers who click on the PPC ads in search.
How Do Search Engines Work?
Google dominates the search market, so what Google thinks and does with its algorithm matters – a lot!
In fact, according to Statistica, Google controlled 87.96% of the search market in 2019.
Search engines like Google use algorithms, or computer programs, to crawl, index, and rank websites based on keywords or phrases entered into the search bar. They send out web crawlers (aka spiders or robots) to find new webpages and record information about them.
Their purpose is to find new webpages that exist and to check the content on pages they have previously crawled to see if there are any changes.
Indexing is when a search engine determines whether the content it crawled on a webpage is worthy of being placed in the search results for a particular term or phrase.
If the content on your webpage is unique and considered valuable, it will be stored in the search engine’s index and made available to show up in a search result.
SEO scammers use “black hat” techniques to try and trick the search engines and the results they display. But search engines like Google are smart and continually update their search algorithms to try to find and punish the websites who use (knowingly or unknowingly) these tactics to manipulate the search results.
Your webpage may not be placed in the index for ranking consideration if:
- Your content is considered duplicate or is significantly identical to what is on another webpage
- Your content is considered to be of low value or spammy in nature
- Your webpage cannot be crawled by the search engine’s spider
- Your webpage or website lacks quality inbound links
Three Fundamental Pillars of SEO
While there are numerous changes and updates made to search engine algorithms each year, the following three optimization factors remain relatively consistent when determining how the search engines find, evaluate, and rank websites:
- Technical SEO Components – The programming factors on your website that impact your SEO performance. How your website is programmed can make a big difference on how well the search engines are able to read your content.
- On-Page SEO Components – The process of ensuring the content on your website is relevant and provides excellent insights that lead to an exceptional user experience. Your content needs to be highly relevant to keywords and phrases used in search, and it needs to be authoritative and timely. It also needs to be formatted in a way that helps the search engines and readers know what’s important, such as using appropriate paragraph headers. And you need to be sure that your content is written with the reader in mind, helping to answer their questions and inquiries. The ultimate goal is to convert a visitor. So, don’t repeat the same word over and over again thinking that is what the search engines want to see. A real visitor will not like that, and neither will the search engines. The search engines recognize themes and synonyms on a webpage, so write naturally and clearly for your reader.
- Off-Page SEO Components – Getting high-quality, authoritative 3rd party websites to link to your website content through do-follow links is extremely important. When other quality sites link to your website, it tells the search engines that you have content worthy of reading, which builds your website reputation and authority as an industry leader.
Ranking Your Webpages
Ranking your webpages is the most critical step.
Your website pages can only be ranked after they have been crawled and indexed by the search engines.
There are more than 200 variables that search engines use to sort and rank web content. All of these variables fall under the three pillars of SEO we mentioned earlier: technical optimization, on-page optimization, and off-page optimization.
Some of these variables include:
- Having the keyword(s) present in the title tag
- The loading speed of the webpage
- Mobile optimization of the webpage
- Using SSL (https://) for page security
- The length of the content on a webpage
- The number of inbound links coming into your website
- The overall website reputation and domain authority
What are the Different Types of Keywords?
When we use the term “keyword” to describe what people enter into the search engine, we are actually referring to a word, phrase, or question that you use to find the information you are seeking.
Most people do not search using just one keyword. Most searches are done using multiple words to better define exactly what someone is searching for.
Increasingly people are searching using a question. In fact, about 30% of “keywords” used in a search are entered as a question, and that number is growing each year.
With the growing adoption of smartphones and virtual assistants (Hey Google, Siri, and Alexa), voice searches are snowballing and will one day dominate the search engines.
So, when we use the term “keywords,” it is really referring to the words used by someone to conduct a search on a particular topic.
There are Three (3) Different Types of Keywords:
- Navigational keywords are searches used to find a specific website or webpage. These types of keywords direct searchers to a place they already have in mind, such as a brand name, a person’s name, or a website address. Examples of these keywords include, “HubSpot,” “hubspot.com,” or “brian halligan hubspot.”
- Informational keywords are used to find information during the awareness stage of the buyer’s journey as a person researches a topic or question to which he or she wants to find an answer. These types of inquiries make up the bulk of online searches. Examples of these searches include, “how to develop a digital marketing strategy,” “digital marketing strategy guide,” or “digital strategy vs. tactics.”
- Transactional keywords are used in searches when a person is closer to making a purchase decision. These searches happen at the decision stage of the buying cycle. Examples of these searches include, “marketing automation platform,” “best CRM,” or “sales software.” They can even include a type of product such as “Dell Laptop Computers,” or “where to buy an iPhone case.”
Type of Keywords Used by Stage of the Buyers Journey

Navigational keywords form the smallest proportion of all keyword searches. They tend to be brand-related and happen at all stages of the buyer’s journey.
If your company or product has significant brand awareness in your market, then people may come directly to your website to search for your products and services. Therefore, you need to make sure you have the right content on your website with effective Calls-to-Action (CTAs) to support moving your buyer through each stage of their buyer’s journey.
Informational keywords form the most substantial proportion of all keyword searches. People use them during the awareness and consideration stage, which are the early stages of the buyer’s journey.
Your website content needs to be more educational in these stages and have effective CTAs to move them to the next stage of their buyer’s journey.
Transactional keywords form a smaller proportion of all keyword searches. They are used during the decision stage of the buyer’s journey when the potential customer is ready to purchase, subscribe, or signup for something you offer.
These keywords are easier to convert to a sale but are more competitive to rank for in search engine queries. In many competitive markets, you may need to have some type of incentive to encourage people to try your product or service.
Let’s Talk More About the SERPs
As we mentioned earlier, the Search Engine Results Pages or SERPs are the results you see after entering your keywords in a search engine like Google. However, there are different types of SERPs.
The layout and results vary based on the types of keywords used in the search, your personal search history, and your location. Results will vary based on these factors as well as the type of device (desktop, tablet, smartphone) used in the search.
There are Three (3) Different Types of SERPs:
- Classical SERPs are what you may see after you search on a keyword or phrase.
- Universal SERPs typically include videos, images, local listings, news, and shopping results.
- Extended SERPs include knowledge graphs, answers to questions, and a related questions box at the bottom of the page.
Classical SERPs
Classical SERPS typically show up after a navigational keyword that includes a brand has been entered into the search box.
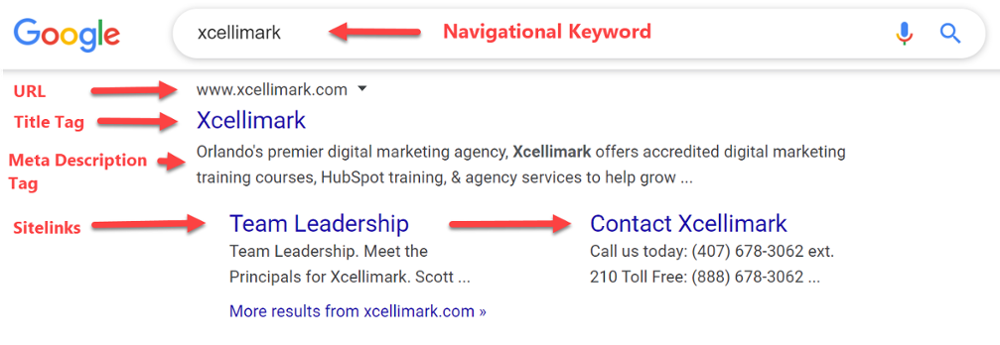
Classical SERPs will consist of elements such as a website URL (website address), title tag, meta description tag, and site links, which are links to internal pages on your website.
Universal SERPs
Universal SERPs may include videos, images, local listings, shopping results, and news.
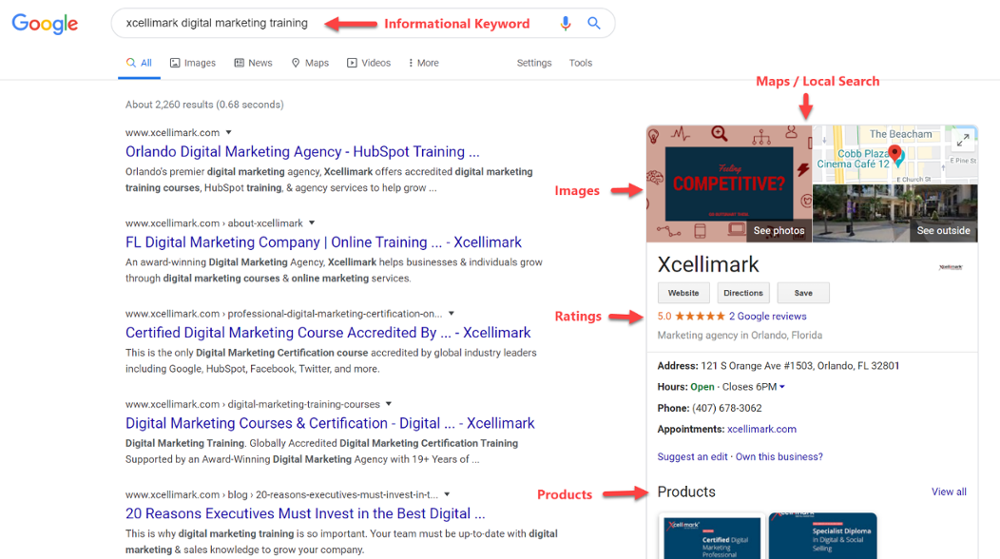
Much of what you see in Universal SERPs depends upon the type of information you are seeking and whether Google assumes that you are looking for a local source.
Setting up and optimizing a Google My Business (GMB) account for your business is a crucial SEO tactic to create more awareness of your company in the Universal SERPs. It can also help you rank well for many informational keywords when Google determines that the person searching is looking for a local provider.
Extended SERPs
Extended SERPs are relatively new, coming on the scene in the last few years.
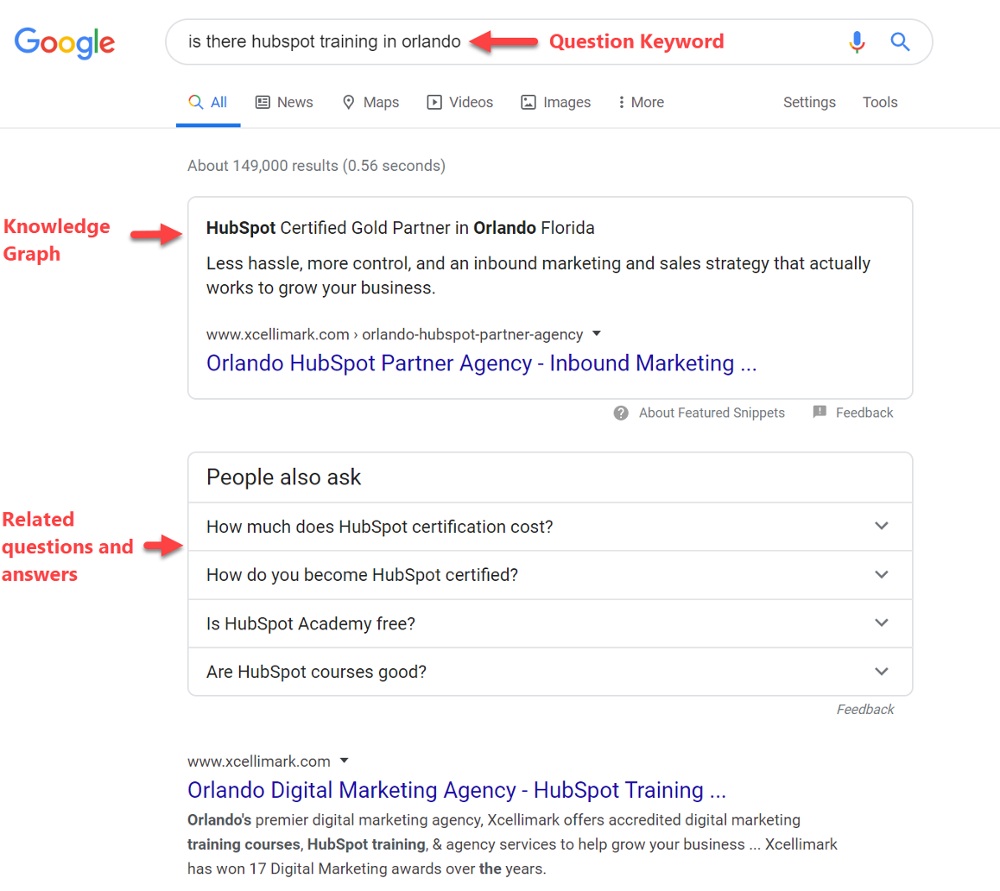
Some of the more common elements in an Extended SERP are knowledge graphs, related questions, and direct answers. Many question-related keywords can also have transactional intent in the decision stage of the buyer’s journey.
The Extended SERP is typically in response to a question keyword. As mentioned earlier, Google has shared that 30% of all searches are question-based keywords.
Question-related keywords are used even more in voice-activated searches with smartphones and virtual assistants. We expect question-based keyword searches to continue to increase as a percentage in overall search.
SEO Fundamentals Summary
Search Engine Optimization is vital to the vast majority of business owners, marketers, and sales professionals.
The benefits of being ranked on page 1 in the SERPs include helping you:
- Create more brand awareness for your company
- Drive more inbound traffic to your website
- Establish your company as an industry leader
- Generate more leads to increase your sales opportunities
The challenge is that a page 1 organic search ranking is not a quick endeavor for a new company, new website, or for a company that has not invested the time and resources to establish a strong website domain authority in the eyes of Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Baidu.
To be successful with your SEO results, you need to:
- Understand the fundamentals of SEO
- Align your SEO efforts with your business objectives
- Identify the keywords and phrases most relevant for your buyers’ journey to build and implement your content marketing plan
- Build your SEO action plan based on the three pillars of technical optimization, on-page optimization, and off-page optimization
- Measure your SEO performance on traffic sources and types of SEO metrics
SEO is not a standalone strategy but rather a key component of your overall digital marketing strategy.
Learn more about how to develop an effective digital marketing strategy to achieve your goals.