Guide to PPC
Fundamentals
Download Your Own Copy
of PPC Fundamentals

Get Started with Google Advertising

Overview
Paid Search advertising campaigns can be a great lead generation tactic for any business, helping lead to more sales opportunities and revenue growth.
Of course, most people think of Google when talking about paid search. That’s because according to Statistica, Google controlled 87.96% of the search market in 2019.
Google Ads is Google’s advertising platform which includes the Pay-Per-Click (PPC) ads that you see on search results as well as Display ads, Gmail ads, and YouTube ads. There is a lot to know if you want to get started with Google Ads, so it’s important to understand how to set up a Google Ads account properly for your PPC campaign to be successful.
Content
Download This as an eBook
Click on the link below to download your own copy of the Guide to PPC Fundamentals.
Download your EbookSince the most popular (and many times the most effective) ads are the ones that show up on Google’s search results, the focus of this guide is to help you get started with a PPC campaign that appears on the Google Search Engine Results Pages (or SERPs).
When you set up a Google PPC campaign, you can burn through some serious cash if you don’t set it up and manage it properly and effectively. That’s why it’s so important to understand at least the basics before you get started.

How Do Pay-Per-Click
Ads Work?

PPC ads are charged each time someone clicks on your ad, thus the term Pay Per Click. (You can also set up payment on a per impression share basis, but most of the time you will want to set it up on a per-click basis.)
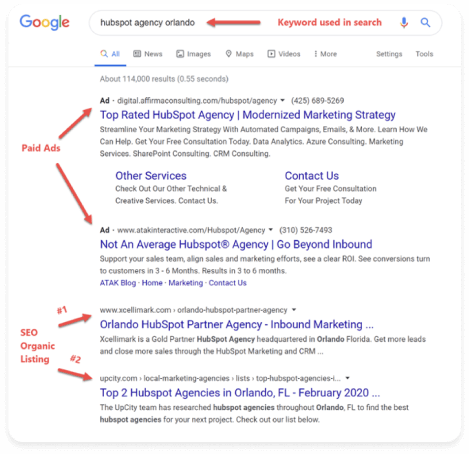
Paid search ads are displayed on Google’s SERPs above, and sometimes below, organic search listings. Organic listings are generated through search engine optimization (SEO) efforts and can take a long time to kick in. Paid search allows you to get to the top of the search engine listing within a few minutes of launching your campaign.
PPC and organic search listings have similarities in how they are displayed in the SERPs, but they are set up and managed very differently.
Here is an example of a SERP based on a keyword search.
You can see that the PPC ads are listed above the organic listings and are marked with the word Ad in front of each advertisement. Then the organic listings are listed below the ads.
There are several different fundamentals involved in effectively setting up a Google PPC campaign. We will touch on seven of these below.
Know Your PPC Campaign Elements

It’s important to understand the key campaign elements you need to develop and implement to run an effective PPC campaign. Each of these elements work together to create a seamless roadmap to reach your desired goal.
If there is a breakdown in continuity in any of these areas, your PPC campaign will most likely suffer and you could end up wasting a lot of money unnecessarily.
These important PPC campaign elements include:
Keywords
Keywords are the words and phrases that are used in searches most relevant to your products, services, and solutions.
Each keyword or phrase that you choose has an associated cost per click.
Depending on how broad you go with your keyword terms, the cost for certain keywords can be quite high and possibly too broad to really be relevant.
That’s why using one word as a keyword is not recommended. You need to use key phrases that are a part of what someone would type into the search box that closely relates to your product or service.
Therefore, even though this term is referred to as “keywords,” you will mostly use key phrases for each term you go after.
We’ll go into more details about keywords in the next section.
Ad Copy
Ad Copy is the content of the ad that people see when they do a search. It includes a Headline and Description.
You can also add additional ad copy by using Ad Extensions. Since you are limited on the number of characters that you can use in your Headline and Description, it’s important to take advantage of using Ad Extensions.
Ad Extensions provide extra space to include more information in your ad and to highlight different features and benefits of your product or service.
Landing Page
A landing page is the website page that you direct a person to when they click on your ad. The copy on your landing page needs to be highly relevant to your ad and to the key phrase being searched on.
Google rates your landing page according to how relevant it feels the page is to each of the keywords you are targeting. Some keywords may be more relevant than others, and each is given a score from 1-10 by Google, with 10 being the most relevant.
Google will charge you more for a keyword that it considers to be irrelevant to your landing page. If the score is very low, then Google may not show your ad at all or very rarely for that particular keyword.
Your landing page also needs to be insightful and compelling to the person who clicks on your ad so they will want to engage with you. Use skillful conversion optimization on your page to ensure that you guide your website visitor down the conversion path that you want them to take.
Calls-To-Actions (CTAs)
Calls-To-Action are links or buttons designed to motivate a person to take action on a webpage or in an email.
Your CTAs should state the action that you want someone to take and indicate what they should expect next when they click on the link.
Try not to use a button that says Submit. That phrase tells the person nothing and does not give them any indication of what to expect next.
Instead, use words that tell the person what to expect such as Read More, Learn More, Download Now, etc.
Always be clear about the action you want someone to take and what they can expect when they take that action.
CTA Example
Forms
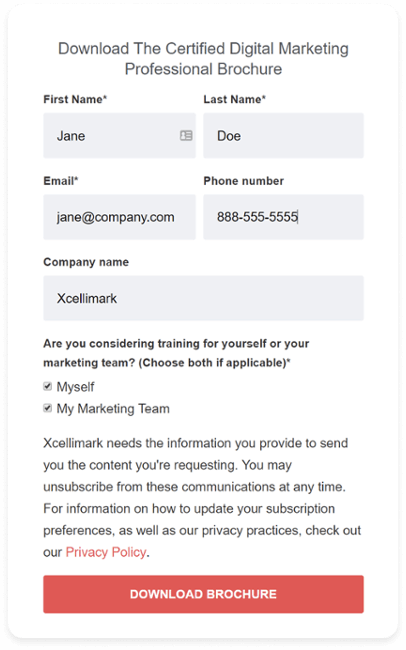
Typically, you should have a form on your landing page to request specific information from a person in response to a CTA.
For example, if your CTA is a link to download a premium content offer, you should request that the person provide some information such as their name and email address on a form in order to download the premium content you are offering.
Keep in mind that you need to be careful about how much information you ask for. Request as much information as you need without asking for more than you need. The more you ask a person to input into a form, the higher friction you will cause on the page and fewer people will complete the form.
There are times when you may want high friction to help really qualify the people completing your form. In those cases, you can be more confident that the people completing the form are motivated to receive what you offer since they were willing to get past the higher friction.
Other times you may want to keep the friction low if your objective is to get as many sign-ups as possible.
So, it’s worth repeating. Ask for as much information as you need without asking for more than you need. If you can get by without asking a particular question, then leave it off the form.
Thank You Page
A Thank You Page is the webpage a person typically views after filling out a form. It is a confirmation page that lets them know they have successfully submitted the form they filled out and have moved to the next step.
This page may include additional information about the offer as well as a link to download the content offer they requested.
You can also use this page to track a conversion. It is assumed that the only way someone will reach the thank you page is if they completed the form on your landing page. Therefore, you can add conversion coding on the thank you page to let Google Ads (and Google Analytics) know that you received a conversion.
This is an extremely important aspect of PPC ads. You need to know which keywords and which ads result in a conversion. You may have a high click-through rate on a keyword and/or ad, but if it doesn’t result in a conversion, then you are essentially paying a lot of money for a keyword and/or ad that are not producing for you.
The end goal for your PPC ad should be a conversion, not just a click. Since you are being charged on a pay-per-click basis, make sure you measure your success all the way through to conversions. It’s easy to do when you use a thank you page.
Autoresponder Email
Autoresponder emails are programmed to immediately send an email to the email address entered into the form on the landing page. This helps accomplish several things.
First, you can verify that the email address entered into the form is valid.
Second, the email provides another confirmation to the person who filled out the form that everything was submitted successfully.
And finally, you can use the autoresponder email to send another link to download the content offer in case they didn’t immediately download it from the thank you page.
There are different types of landing pages, CTAs, forms, thank you pages, and autoresponder emails based on the goal you are hoping to achieve with your PPC campaign. Also, the experience of viewing a landing page is different on a mobile device compared to a desktop computer.
Therefore, you need to provide a great mobile experience that is simple and easy for the person to use. That includes using a CTA that is large enough to easily click with your thumb and font sizes that are readable on smaller screens.
Google Ads evaluates how well your landing page is optimized for mobile devices, so ensure
your landing page is responsive for all size screens. If your landing page is not optimized for mobile users, this will lower your quality score for mobile traffic and can have a negative impact on your PPC campaign.
Set Up Your Google
Ads Paid Search
Account Properly

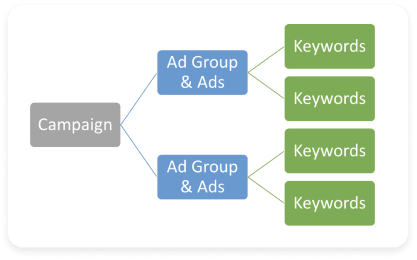
There are three (3) main components inside Google Ads that need setting up before you can go live with your ads. These components include:
- Campaigns
- Ad Groups and Ads
- Keywords
The Campaign is the first thing that you will create when setting up a PPC ad. Everything under the campaign should relate to the main campaign topic. You can set up multiple campaigns within your account, so it’s important to keep your themes separated by campaign.
Under each campaign are Ad Groups. Each ad group includes Keywords and Ads. You can have multiple ad groups under each campaign, so it’s important to focus your ads and your keywords on themes and then split those themes into different ad groups.
By splitting your themes into different ad groups, you can keep your keywords, ads, and landing pages relevant to the theme of the ad group.
Remember, Google looks at how relevant your keywords are to your landing page and ranks each keyword accordingly with a relevancy score. The higher your relevancy score, the less you may have to pay for that keyword.
Here are other key elements of your account that impact your campaigns:
Match Type
These are parameters that are set on your keywords to control which searches trigger your ads to appear. There are four different match types – broad match, exact match, phrase match, and a modified broad match.
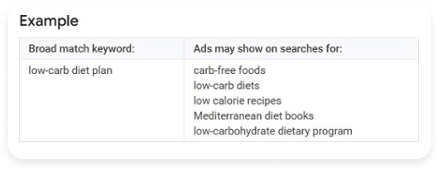
- Broad match is the default match type that your keywords are assigned if you don't specify another match type. With broad match, Google shows your ads on variations of your keywords, including synonyms, possible misspellings, stemmings (such as floor and flooring), and other related searches. Be careful with broad match because you can sometimes get clicks from searches that are not relevant for you. But you can start with broad match, check the search terms being used, then add the non-relevant terms as negative keywords.
- Exact match shows your ad to people searching for your exact keyword, or close variants of your exact keyword. Close variants include searches for keywords with the same meaning as the exact keywords, regardless of spelling or grammar similarities between the query and the keyword.
You have the most control over your keywords with exact match.
- Phrase match allows you to show your ads to customers searching for your exact keyword and close variants of your exact keyword, with additional words before or after. Phrase match is more targeted than the default broad match, but more flexible than exact match. It gives you more control over how closely the keyword must match someone's search term so your ad can appear. This is a good compromise between being too broad or too narrow.
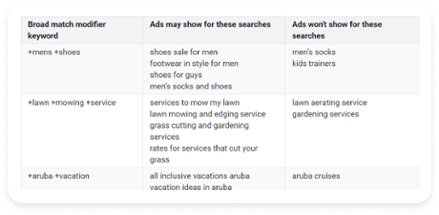
- Modified broad match is a variation of regular broad match. This option ensures that your ads only show in searches that include the words you’ve marked with a plus sign, such as +red +shoes, or close variants of these terms. Additional words may appear in the search before, after, or in between your “+” terms. For example, the broad match modified keywords +red +shoes can match a search for “shoes for sale that are red” or “red men’s shoes,” but not for “blue shoes” or “red hiking boots.”
Negative Keywords
These are keywords that might be related to your campaign, but you want to exclude them from your campaign and not have them display your ads when someone searches with this keyword. For example, you may have a service that you are advertising, but it’s not free. So, you can add the word “free” as a negative keyword to your campaign or ad group.
Adding negative keywords is important to your campaigns because they help reduce unwanted clicks from unwanted searches. You can reduce costs, increase your click-through rates (CTRs), and manage your paid search activity more effectively when you add negative keywords.
Note – after your ads have run for a little while, check the search terms being used when someone clicks an ad by clicking Search Terms under your Keywords tab. You may find additional keywords that you want to add to your negative keyword list.
Max Cost-Per-Click (CPC) Bids
When you set up your ad group, you will be asked to set a maximum bid that you are willing to pay for each click. This helps to control your costs.
You can set bids on two (2) different levels – Ad Group level and Keyword level. The keyword level bid will override your ad group level bid for a particular keyword.
Ad Copy
The content of the ad that someone sees when they perform a Google search is your Ad Copy. It includes a Headline and Description. Responsive Ads allow you to include multiple headlines and multiple descriptions, which Google will then put together in various combinations.
Headlines are limited to 30 characters and descriptions are limited to 90 characters.
Well-written ads are vital to improving your brand and generating more clicks on your ads to drive traffic to your website or landing page. It’s important to create at least three (3) ads per ad group in order to test which messaging gets the most clicks and ultimately the most conversions.
Definitely include any ad extensions that make sense with your ad group and campaign.
Ad Extensions
These are enhanced features that make your ad more appealing and help drive higher click-through rates. You should look at the types of extensions available to you and choose the most appropriate one for your business and your goal.
Extensions can bring more life to your ads by allowing you to add more content since the headline and descriptions have character limitations.
Ad extensions include such things as your phone number, location, map, products, and links to specific pages on your website. Extensions appear below your ad copy and can increase the size of your ad to make it more noticeable, which helps engage more people.
Do Your Keyword
Research

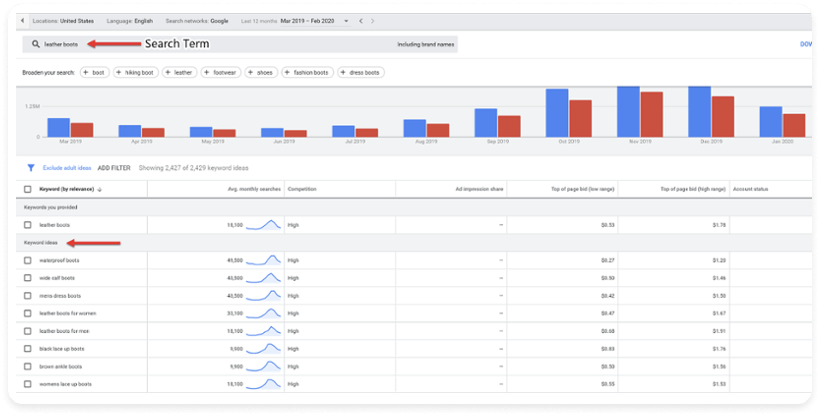
Keyword research is the process by which you identify and determine which keywords are most related to your product or service. One tool to use for your keyword research is the Google Keyword Planner.
There are other good keyword research tools that are available for a price, including SEMRush and Wordtracker.
When setting up your campaign, the Google Keyword Planner allows you to identify keywords currently being used that it deems are relevant to your company, products, and services. The Google Keyword Planner is integrated into your Google Ads account and allows you to easily add keywords into your keyword list for each ad group.
The Keyword Planner also estimates monthly search volume based on your maximum bid and monthly budget for each keyword it recommends. This helps you start building out an assumption-based forecasting model to determine your potential website visits based on your estimated CTR.
At this point, you want to map your buyer's journey to project your funnel stages, such as visits, leads, sales opportunities, deals, and sales forecasts. Identify your keywords according to the different stages of the buyer’s journey, which includes Awareness, Consideration, and Decision. You can then create different ad groups and ads for each buyer’s journey stage.
Creating
Your Campaign

There are key settings that you will fill out when creating your campaign.
These are campaign settings that are not available on the ad group level. Campaign settings allow you to customize your campaign to target your ideal buyers more effectively to meet your goals.
Campaign Settings Include:
- Name
Name the campaign carefully to easily remember the theme and target of the campaign.
- Location
Decide which geographic locations are ideal for your company and your campaign.
- Language
Identify the languages of your primary buyers.
- Daily Budget
Determine how much you are willing to spend daily to manage your monthly budget.
- Goal
Outline the goals you want to achieve. Different goals can be related to Sales, Leads, Website Traffic, Product and Brand consideration, Brand awareness and reach, and App promotion. Setting a goal is optional in your campaign, but Google will better under- stand what you are trying to achieve with the campaign if you identify the goal.
- Networks
You will tell Google which networks you want your ads to appear on. The networks include Google Search, Google’s Search Partners, and the Display network. We recommend choosing the Google Search and Google Search Partners networks when setting up your campaign. The Display network works differently and should be set up in a separate campaign.
Manage Your Paid
Search Campaign
The key areas that impact the cost of your PPC campaign are budget, bidding, and optimization of the campaign.
Budget management includes how much you are willing to spend on a daily and monthly basis. It can always be adjusted, but you need to set a budget. Your budget will impact overall traffic and results since Google will attempt to stay within your set budget.
If your budget is lower than what Google estimates it will take to show your ad in every relevant search throughout the day, then Google will stagger your ad to only appear the number of times during the day it thinks will keep your campaign within budget.
If you have categorized your ad groups and keywords according to the stage of your buyer’s journey (Awareness, Consideration, Decision), you can allocate your budget according to these stages. For example, you may want to allocate 20% of your budget to the Awareness stage key- words, 20% to the Consideration stage, and 60% to the Decision stage.
Your cost per click is based on Google’s bid auction.
The bid auction is where your competitive advertisers bid and compete for the clicks on your keywords. There are several factors Google uses to determine the actual cost-per-click (CPC).
- Maximum CPC set by the advertiser
- The quality score of the advertiser
- The relevance of their ads
- Ad rank and other variables
Ad rank and quality score are two important metrics that Google uses to determine your final CPC.
To get a high ad rank and quality score, your ad and your website or landing page content must be highly relevant to the keyword on which you are bidding. Google also considers your click-through rate (CTR) for each ad and keyword when determining your cost-per-click.
The bid simulator tool is a useful tool that provides insights into setting bidding thresholds, estimated results, and costs.
Optimizing your campaign is critical to achieving your desired results. One of the most common mistakes people make in a PPC campaign is setting up the campaign and then not optimizing it by continuing to monitor, track results, and conduct testing.
You should test different ads inside each ad group to get the best CTR and test different landing pages to achieve the best conversion rates.
A/B Split Testing is a highly effective method of ensuring that the campaigns deliver the desired results you seek. A/B testing is a marketing experiment where your audience is split to test different variations of the campaign to determine which one performs better.
For example, you can show version A of a landing page to 50% of your audience and version B to another 50% of your audience. You then determine which version has the best performance rate for that marketing experiment.
You can also test your ads against each other to see which has a higher CTR. As mentioned earlier, we recommend that you create and test at least three (3) ads for each ad group. Then pause the ad that is not doing as well as the others and add another ad to test.
So, you can test your landing pages to see which has the highest conversion rate and your ads to see which have the best click-through-rate and conversion rate.
Why guess when you can test?
Measure Your Paid
Search Campaigns
with KPIs

Tracking, measuring, and analyzing your campaign results are critical to your overall campaign success. Ultimately, you want conversions based on your goal.
A conversion can be someone buying something, signing up for something, or filling out a form to receive something. Calculating your conversion rate and the cost associated with your conversion rate is a key business measurement.
However, there are many key performance indicators (KPIs) that impact your conversion rate. These KPIs should be identified, tracked, and measured.
Your KPIs Could Include:
- Impressions
The number of times an ad is displayed to your audience.
- Clicks
How often an ad is clicked.
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC)
The actual price paid for each click in your PPC campaign.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
The percentage number of impressions that lead to a click.
- Cost-Per-Impression (CPM)
The cost of serving your ad per 1,000 impressions.
- Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA)
The PPC media spend to generate an action such as a conversion or sale.
- Average Position
Where an ad is shown on a search result page.
- Conversion
An action that an advertiser defines as valuable once someone clicks on an ad, such as a purchase or form completion.
- Cost-Per-Conversion
An action that an advertiser defines as valuable once someone clicks on an ad, such as a purchase or form completion.
- Impression Share
The number of impressions received divided by the estimated number of impressions that were available.
- Click/Impression-Assisted Conversions
The number of conversions that were assisted by a campaign, ad group, or keyword.
- Quality Score
An estimate of how relevant your ads, keywords, and landing page are to a person seeing your ad.
These KPIs are tracked at a campaign, ad group, and keyword level to measure the success of your PPC campaigns.
An additional recommendation we typically make is to connect your Google Ads account with your Google Analytics account. This allows you to go even deeper in gaining actionable intelligence.
If you have a Marketing Automation Platform such as HubSpot, you can connect your Google Ads account to your HubSpot account, allowing you to measure your conversions by actual people and not just numbers.
Measure Your
Success on Sales
and Customer
Success
Ultimately, you need to measure your PPC campaign success based on the sales and revenue it generates. This can be challenging if your marketing and sales team do not align their processes and use the same tracking and measuring tools or technology.
There are different stages a buyer goes through before they decide to purchase. Not all leads are the same and each must be qualified. And every company has different marketing and sales stages.
The marketing and sales stages should be mapped out and tracked systematically. If done correctly, you can determine your cost of sale or acquisition based on the PPC campaign, ad group, and even keyword.
Based on the results, you can then determine the ideal path for your best customers and make the necessary changes in your PPC campaign to optimize it for even better results.
Summary
Setting up and running a PPC campaign today can be complicated—but rewarding—if done correctly. It has the potential to help you generate more leads and customers faster.
It does require you, your team, or your agency to measure, track, analyze, and determine if changes need to be made. These actions must be taken on almost on a daily, and certainly a weekly basis, to make sure the campaign is optimized for best results.
Your PPC campaign is not a strategy. It is a digital marketing tactic that is part of your Digital Marketing Strategy and Plan.
Get in-depth training on Google PPC along with all the other aspects of being a Digital Marketing Professional today. Click on the link below to learn more.